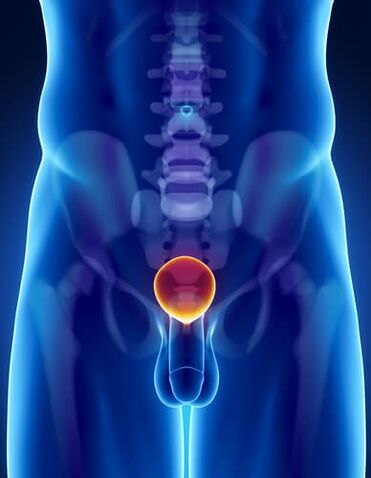
ProstatitisIs a urinary pathology accompanied by inflammation of the tissues of the prostate gland. Prostate damage can be caused by infection transmitted through blood, lymph, or unprotected sex. The development of prostatitis in men is facilitated by trauma and impaired blood supply to the pelvic organs, persistent hypothermia, lack of physical activity, hormonal imbalances andother factors. Prostatitis can be accompanied by inflammation of the seminal vesicles, urethritis and other infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive organs and urinary tract.
Rate statistics
Prostatitis is one of the most common diseases of the male genitourinary system in the world. According to various sources, it is observed in 60-80% of sexually mature men. According to official medical statistics, over 30% of young people of reproductive age suffer from chronic prostatitis. In about a third of cases, it occurs in men over the age of 20 and under 40. According to WHO, urologists diagnose chronic prostatitis in every tenth of patients.
Causes of inflammatory prostate disease
Infection.The bacteria cause disease and the opportunity to penetrate the prostate gland through the lymphatic system and blood vessels. Secondary prostate infection is often a complication of inflammatory diseases of the rectum and urethra.
Types of infection:
- ascendingbacteria come up the gland from the outer urethral opening;
- downwardThe bacteria enter the prostate gland with the infected urine stream.
Pathogenic microorganisms with pathogenic conditions (according to the Institute of Urology Research 1997-1999)
| Microorganism | Number of studies | |
|---|---|---|
| % | abdominal muscles | |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 42. 3 | 55 |
| S. saprophyticus | 17, 6 | 23 |
| S. aureus | forty six | 6 |
| S. haemolyticus | thirty first | four |
| S. hominis | 0, 8 | one |
| S. warneri | 1, 5 | 2 |
| Staphylococcus spp. | thirty first | four |
| Enterococcus faecalis | 11, 6 | fifteen |
| Streptococcus spp. | thirty first | four |
| TOTAL (gr. +) | 87, 6 | 114 |
| P. aeruginosa | 3. 7 | five |
| E coli | 4, 7 | 6 |
| Enterobacter spp. | 2, 3 | 3 |
| Proteus spp. | 1, 5 | 2 |
| TOTAL (gr. -) | 12. 3 | sixteen |
Impaired immunity.One of the causes of prostatitis is weakened immune defenses. This can be motivated by frequent stress, unbalanced diet, overwork, smoking, or drinking alcohol. With impaired immunity, the body is most susceptible to infections that lead to prostate disease development.
Disorders of blood supply.The development of chronic prostatitis can be a result of a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle. In the absence of continuous physical activity, the work of the endocrine, cardiovascular and nervous systems, as well as blood circulation in the pelvic organs, is interrupted. As a result, prostate tissue becomes oxygen starved.
Sporadic sexual activity.Both prolonged abstinence from sex and excessive sexual activity can contribute to prostatitis. Many men, when having sex, suffer from nervous breakdown, hormonal imbalance, impaired secretion of the gonads and decrease in potency. Interrupted intercourse has an adverse impact on the health of the prostate gland.
Chronic prostate damage. . . Chronic prostatitis can develop as a result of frequent trauma to the soft tissues of the prostate gland. This is often observed in patients with a driver-related occupational activity. The cause of prostatitis in this case is vibration, constant shaking and excessive stress on the pelvic floor muscles.
The main syndromes of prostatitis
Pain.With prostatitis in men, soreness and cutting pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, as well as soreness all over the body. This symptom may be exacerbated by ejaculation, especially during intercourse after prolonged abstinence.
Difficulty urinating. The typical signs of prostatitis in men are frequent urination, burning and burning pain when emptying the bladder, burning pain after urinating in the epis. Another symptom of prostatitis is difficulty urinating. In the absence of treatment, acute urinary retention may occur.
Sexual dysfunction.With uncomplicated prostatitis, ejaculating faster, wearing an orgasm, pain during ejaculation, a partial or complete decrease in libido. Prolonged night-time erections are also a symptom of chronic prostatitis.
External manifestations.With prostatitis, some patients have a purulent or transparent discharge from the urethra, most in the morning. The patient may also notice a symptom such as the presence of white flakes or fibers in the urine.
Types of prostatitis
Acute bacteria.Acute prostatitis develops due to infection of the prostate gland with Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, enterococcus and other pathogenic bacteria. If left untreated, the disease can cause blood poisoning. In this case, the man needs to be hospitalized urgently.
Symptoms observed with this type of prostatitis:
- chills and fever (38 ° C or higher);
- throbbing or pulling pain in the groin, lower back, and perineum;
- frequent urination;
- painful urination;
- difficulty urinating and acute urinary retention;
- white or colorless discharge from the urethra.
Chronic bacteria.The recurrent form of the disease occurs due to the penetration of the infection into the gland. Chronic hypothermia, prolonged sexual abstinence and untimely urination contribute to the development of prostatitis. Chronic prostatitis, if left untreated, can cause cystitis, as inflammation in the prostate gland is a reservoir of bacteria that affect the genital tract.
Symptoms of chronic prostatitis:
- pain in the scrotum, lower abdomen, perineal area;
- difficulty urinating;
- validity violation.
Chronic not caused by bacteria.The causes of the disease include the penetration of a virus or bacteria into the prostate gland (tuberculosis bacillus, Trichomonas, chlamydia), autoimmune processes, penetration of urine into the gland. Chronic prostatitis accounts for 95% of all prostatitis.
The signs of prostatitis are:
- Chronic pain in the pelvic region (bothering the man for at least 3 months);
- recurrent groin pain;
- There are no inflammatory symptoms in urine secretions, semen, and prostate.
Chronic asymptomatic.Asymptomatic chronic prostatitis is not associated with bacterial infection and symptomatic prostate syndromes. It is hypothesized that this disease is an age-related physiological trait.
Symptoms of this type of chronic prostatitis:
- there is no major syndrome of the disease;
- increased content of leukocytes and bacteria in the urine.
The main symptom of the disease - the presence of infection in the gland - can be detected only by biopsy or during surgery to treat various diseases of the prostate gland (adenoma, cancer).
Stagnant.Prostatitis develops not only on the basis of anatomical and physiological changes in other venous and bodily systems. The main cause of the disease is due to an irregular sex life.
Signs of prostatitis:
- pain in the perineal region, spreading to the sacral region;
- increased morning urination;
- mild difficulty in the outflow of urine (symptoms are observed in a chronic form of the disease);
- impaired erection ability;
- decreased libido;
- "Pallor" of the feeling of orgasm on ejaculation.
Diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis
In order to choose the correct method of treatment, the doctor appoints a comprehensive diagnosis of the condition of the genitourinary system, including the following methods.
Digital rectal examination.If you suspect prostatitis, your urologist will perform a digital examination. The back of the prostate gland is adjacent to the rectum, so when a finger is inserted through the anus, the doctor can determine the condition of the gland. During the study, its size, consistency and shape, surface condition, and pain are determined.
Signs of prostatitis in men include:
- soft, inelastic prostate gland;
- pain when palpable;
- extended route;
- immobility of the rectal mucosa on the prostate gland.
Ultrasound process.Prostate ultrasound is prescribed before the start of treatment for acute prostatitis to identify / rule out an abscess and in the chronic period of the disease - to identify prostate cysts and stones, alsosuch as the degree of urethral compression. The most effective method is transrectal ultrasound.
Urine flow measurement.This method of prostatitis is used to study the indicators of the urination process: the duration of this physiological action and the rate at which urine comes out. If the velocity is 15 ml / s or more, this indicates a normal urethra. A sign of prostatitis is a drop below 10 ml / s. This rate is the result of poor urinary regulation.
Interpret urinary flow measurement results
| The flow rate of urine | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| >15ml / sec | Unsure urinary tract obstruction |
| <10ml / sec | There is a possibility of significant urethral narrowing or genital muscle weakness. |
| 10-15ml / sec | Unspecified results |
Cystoscopy.To check, an endoscopic imaging system is inserted into the bladder. This method of diagnosis of acute and chronic prostatitis is used when conditions such as cancer, cystitis or bladder injury are suspected.
Research in the laboratory.To diagnose and identify the microorganism that causes the disease, when there are symptoms of chronic prostatitis or acute inflammation, urine and prostate secretions are examined. An indication of the presence of pathogenic microflora is an increased number of leukocytes in the biological material. To build an effective treatment process, bacteria were identified by PCR, RIF and inoculated on nutrient medium.
Interpret laboratory results
| Prostate secret | Third urine sample (after prostate massage) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Form HP | WBC count, uv. x 400 | Sow the results | WBC count, uv. x 400 | Sow the results |
| Bacteria | >ten | + | The difference between the number of leukocytes in the third urine portion and the second urine portion is ≥10 | + |
| Chronic pelvic pain inflammatory syndrome | >ten | - | The difference between the number of leukocytes in the third urine portion and the second urine portion is ≥10 | - |
| Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is not caused by inflammation | <10 | - | - | - |
Prevention of prostatitis

Physical activity.For the prevention and treatment of prostate disease, a man must avoid being sedentary. Recommendations:
- walking (4 kilometers per day or more);
- exercise (squatting, jumping, bending);
- pelvic and buttocks muscle training (10 stretches and relaxation).
Proper nutrition.To prevent acute and chronic prostatitis, men should supplement their diet with foods rich in zinc and vitamin B. Eat:
- seafood (oysters, seaweed);
- meat;
- pumpkin seeds;
- Walnuts;
- bran;
- kefir;
- Rye bread.
Regular sex life.When preventing and treating the disease, men need:
- have a smooth sex life;
- avoid interrupted sex;
- avoid romantic relationships.
Treatment of acute and chronic prostatitis
Prostatitis is treated with the following methods.
Antimicrobial therapy.If bacterial prostatitis requires antibiotics for treatment. The doctor chooses a class of drugs depending on the type of pathogenic bacteria, the sensitivity of the pathogen to different drugs and the presence of contraindications in the patient.
Characteristics of the drug
| A kind of medicine | Benefits | defect |
|---|---|---|
| Fluoroquinolon |
|
|
| Macrolide |
|
Ineffective against gram-negative bacteria |
| Tetracyclines | Active against atypical pathogens |
|
Hormone therapy.Hormonal treatment is needed to restore a normal hormonal balance between androgens and estrogen. The drug has antigenic activity that reduces inflammation of the tissues of the gland and prevents the disease from progressing to a more severe stage.
Massage the prostate gland.This method of treatment for chronic prostatitis is only possible with external exacerbations. A man should be in a leaning position, with palms resting on a bench or table, with his feet shoulder-width apart. The doctor conducts treatment to put sterile gloves on the hand, apply ointment or gel (in some cases drugs with anesthetic ingredients) to the index finger of the right hand and inject through the anus into the rectum. The massage is done by gently pressing until the secretions of the prostate gland are separated through the urethral opening. Treatment includes at least 10 massages.
Physical therapy.To treat symptoms of prostatitis, methods are used to normalize and increase blood circulation in the pelvic region. This allows you to eliminate stagnation, as well as increase the effectiveness of drug treatment. Treatment is carried out by exposing the gland to ultrasound waves, electromagnetic vibrations, as well as high temperatures (differential with warm water).
Surgical intervention.Surgical interventions for prostate disease are rarely used. Such treatment is required when developing complications of acute or chronic prostatitis.
Indications for prostate surgery:
- Urinary retention as a result of severe narrow urethra;
- abscesses (the appearance of compression on the surface of the gland);
- sclerosis of the glands;
- Adenoma did not respond to conservative treatment.
Complications of prostatitis

Inflammation of blisters.Untreated prostatitis can cause inflammation in the seminal vesicles. Symptoms of the disease are pain deep in the pelvis, spreading to the sacrum, exacerbated with erections and ejaculation, frequent urination, blood and / or pus present in semen and urine.
Colloiditis and urethritis.Because they are located near the secretory lines of the prostate gland, the tubers are often inflamed by infection from the infected gland. If left untreated, symptoms of prostatitis are complemented by the characteristic symptom of urethritis - burning or tickling in the urethra when urinating. There is also pain during ejaculation due to convulsions of the urethra.
Prostate abscess.On the surface of the route appears purulent cavities which are caused by bacteria that cause prostatitis. A characteristic symptom of the disease is general weakness, impaired consciousness, delirium, a sharp rise in temperature, increased sweating, and chills. Prostate abscess is a serious infection that must be treated in hospital.
Prostate sclerosis.Prostate sclerosis develops against the background of frequent exacerbations of chronic prostatitis due to noncompliance with treatment prescribed by the urologist. This disease can form in a few years, however, if the hormonal balance in a man's body is disturbed it can develop rapidly. With prostatic sclerosis, you may experience pain when your bladder is empty, and the urine flow is intermittent and slow.
Formation of cysts and stones. . . The appearance of cysts in the gland is one of the possible options for the progression of chronic prostatitis. Infection with the tumor can cause abscesses and greatly complicate the treatment of the disease. A single stone and multiple stones can also form in the prostate gland. In this disease, in addition to the usual symptoms of chronic prostatitis, there are also violations of the flow of urine, frequent urination, pain in the epis.
Dry.In chronic prostatitis, sperm production and motility are impaired. If left untreated, the disease also affects the vas deferens and seminal vesicles, making the sperm unable to pass so it cannot be passed into the urethra during ejaculation. Therefore, men with chronic prostatitis are often infertile.